Overview
Besides gene-based annotations, ANNOVAR has several other utilities, such as region-based annotation. This function is issued by the --regionanno argument (by default, --geneanno is ON)
It is important to explain the difference between region-based annotation and filter-based annotation here. Filter-based annotation looks exact matches between a query variant and a record in a database; two items are identical only if they have identical chromosome, start position, end position, ref allele and alaternative allele. Region-based annotation looks for over lap of a query variant with a region (this region could be a single position) in a database, and it does not care about exact match of positions, and it does not care about nucleotide identity at all. So in a sense, region-based annotation is somewhat similar to tabix, except that it does have involve index so it is much slower, yet it allows more user configuration to fine-tune results.
Generally speaking , users can select annotation tracks that are already provided by the UCSC Genome Browser annotation databases. Most of these annotation tracks have similar file formats, but sometimes they differ (for example, different number of columns in the file). ANNOVAR will try to be smart in guessing the correct column headers, and usually it works well. However, ANNOVAR may also provide built-in region annotation databases, which can be downloaded by -downdb -webfrom annovar. Finally, users can supply your own region annotation databases in generic, BED or GFF formats.
Conserved genomic elements annotation
One of the particularly useful function is to identify variants at conserved genomic regions. For this analysis, users can choose several different annotation tracks. For example, when handling human genomes, users may want to choose tracks such as the 17-way / 28-way / 44-way most conserved track (for NCBI 36 genome assembly), or 46-way / 46-way primates / 46-way placental / 100-way alignment (for NCBI 37 genome assembly). ANNOVAR will attempt to identify the subset of variants that either fall within the conserved regions (for SNPs and short in-dels), or overlap with these conserved regions (for large-scale CNVs, and the extent of overlap is user-configurable).
Technical Notes: these are phastCons conserved elements, which means specific genomic regions that are conserved. These are different from base-level conservation scores which are typically referred to as PhyloP scores. For base-level conservation scores, ANNOVAR provides filter-based annotation for exonic variants.
Here ANNOVAR uses phastCons 46-way alignments to annotate variants that fall within conserved genomic regions. Here the --regionanno argument need to be supplied so that the program knows what to do. In addition, the --dbtype need to be specified so that the program knows which annotation database file to interrogate. Make sure that the annotation database is already downloaded (the command is annotate_variation.pl -downdb phastConsElements46way humandb/).
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ annotate_variation.pl -build hg19 -downdb phastConsElements46way humandb/
NOTICE: Web-based checking to see whether ANNOVAR new version is available ... Done
NOTICE: Downloading annotation database http://hgdownload.cse.ucsc.edu/goldenPath/hg19/database/phastConsElements46way.txt.gz ... OK
NOTICE: Uncompressing downloaded files
NOTICE: Finished downloading annotation files for hg19 build version, with files saved at the 'humandb' directory
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ annotate_variation.pl -regionanno -build hg19 -out ex1 -dbtype phastConsElements46way example/ex1.avinput humandb/
NOTICE: Reading annotation database humandb/hg19_phastConsElements46way.txt ... Done with 5163775 regions
NOTICE: Finished region-based annotation on 12 genetic variants in ex1.hg19.avinput
NOTICE: Output files were written to ex1.hg19_phastConsElements46way
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ cat ex1.hg19_phastConsElements46way
phastConsElements46way Score=387;Name=lod=50 1 67705958 67705958 G A comments: rs11209026 (R381Q), a SNP in IL23R associated with Crohn's disease
phastConsElements46way Score=420;Name=lod=68 16 50756540 50756540 G C comments: rs2066845 (G908R), a non-synonymous SNP in NOD2
phastConsElements46way Score=385;Name=lod=49 16 50763778 50763778 - C comments: rs2066847 (c.3016_3017insC), a frameshift SNP in NOD2
phastConsElements46way Score=395;Name=lod=54 13 20763686 20763686 G - comments: rs1801002 (del35G), a frameshift mutation in GJB2, associated with hearing loss
phastConsElements46way Score=545;Name=lod=218 13 20797176 21105944 0 - comments: a 342kb deletion encompassing GJB6, associated with hearing loss
The output is saved in the ex1.hg19_phastConsElements46way file. The first column in the output is "phastConsElements46way" indicating the type of annotation. The second column contains two pieces of information: Score and Name. Score is the normalized score assigned by UCSC Genome Browser, and this score range from 0 to 1000 for the sole purpose of having a standard range of values to display in browser. (Note that the --score_threshold or --normscore_threshold can also be used to filter out specific variants with low conservation scores.) The "Name=lod=x" is used to tell the user a name for the region (in this case, I assign the "name" as the LOD score because the region does not have an extra name). All other columns are identical as those in the input file. Only variants that actually are located within a conserved region will be printed in the output file. As a result, only 5 variants are in the output file.
Let's try using the -normscore_threshold:
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ annotate_variation.pl -regionanno -build hg19 -out ex1 -dbtype phastConsElements46way example/ex1.avinput humandb/ -normscore_threshold 400
NOTICE: Reading annotation database humandb/hg19_phastConsElements46way.txt ... Done with 1151862 regions (that passed --score_threhsold or --normscore_threshold from a total of 5163775 regions)
NOTICE: Finished region-based annotation on 12 genetic variants in ex1.hg19.avinput
NOTICE: Output files were written to ex1.hg19_phastConsElements46way
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ cat ex1.hg19_phastConsElements46way
phastConsElements46way Score=420;Name=lod=68 16 50756540 50756540 G C comments: rs2066845 (G908R), a non-synonymous SNP in NOD2
phastConsElements46way Score=545;Name=lod=218 13 20797176 21105944 0 - comments: a 342kb deletion encompassing GJB6, associated with hearing loss
As you will see, only two variants are in output file now.
Technical Notes: The exact columns that should be in output file (Name=?) can be controlled by the -colWanted argument. The exact column for the scores (Score=?) can be controlled by the -scorecolumn argument. For some annotation (such as phastCons conserved elements), ANNOVAR already sets up default values, such as in the example above. For some other less used annotation, the default from ANNOVAR may not work for the user, and you can use the -colWanted and -scorecolumn argument to fine-tune the annotation output.
For each genome build, the user needs to specify the correct argument. For example, when dealing with hg19 coordinate, you can check http://hgdownload.soe.ucsc.edu/goldenPath/hg19/database/ for all supported databases. Let's try 100-way elements this time:
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ annotate_variation.pl -regionanno -build hg19 -out ex1 -dbtype phastConsElements100way example/ex1.avinput humandb/
NOTICE: Reading annotation database humandb/hg19_phastConsElements100way.txt ... annotate_variation.pl -regionanno -build hg19 -out ex1 -dbtype phastConsElementDone with 10107363 regions
NOTICE: Finished region-based annotation on 12 genetic variants in ex1.hg19.avinput
NOTICE: Output files were written to ex1.hg19_phastConsElements100way
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ cat ex1.hg19_phastConsElements100way
phastConsElements100way Score=388;Name=lod=54 1 67705958 67705958 G A comments: rs11209026 (R381Q), a SNP in IL23R associated with Crohn's disease
phastConsElements100way Score=468;Name=lod=121 16 50756540 50756540 G C comments: rs2066845 (G908R), a non-synonymous SNP in NOD2
phastConsElements100way Score=423;Name=lod=77 16 50763778 50763778 - C comments: rs2066847 (c.3016_3017insC), a frameshift SNP in NOD2
phastConsElements100way Score=327;Name=lod=29 13 20763686 20763686 G - comments: rs1801002 (del35G), a frameshift mutation in GJB2, associated with hearing loss
phastConsElements100way Score=592;Name=lod=422 13 20797176 21105944 0 - comments: a 342kb deletion encompassing GJB6, associated with hearing loss
Transcription factor binding site
Similarly, annotation of TFBS can be done by the commands below. Download the database if it is not already downloaded. Users should be aware that there are many different types of TFBS annotations that ANNOVAR can use. See FAQ entry for more explanation. The example below uses the tfbsConsSites region annotation, which contains the location and score of transcription factor binding sites conserved in the human/mouse/rat alignment, where score and threshold are computed with the Transfac Matrix Database. See details here.
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ annotate_variation.pl -build hg19 -downdb tfbsConsSites humandb/
NOTICE: Web-based checking to see whether ANNOVAR new version is available ... Done
NOTICE: Downloading annotation database http://hgdownload.cse.ucsc.edu/goldenPath/hg19/database/tfbsConsSites.txt.gz ... OK
NOTICE: Uncompressing downloaded files
NOTICE: Finished downloading annotation files for hg19 build version, with files saved at the 'humandb' directory
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ annotate_variation.pl -regionanno -build hg19 -out ex1 -dbtype tfbsConsSites example/ex1.avinput humandb/
NOTICE: Reading annotation database humandb/hg19_tfbsConsSites.txt ... Done with 5797266 regions
NOTICE: Finished region-based annotation on 12 genetic variants in ex1.hg19.avinput
NOTICE: Output files were written to ex1.hg19_tfbsConsSites
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ cat ex1.hg19_tfbsConsSites
tfbsConsSites Score=767;Name=V$PAX5_02 16 50745926 50745926 C T comments: rs2066844 (R702W), a non-synonymous SNP in NOD2
tfbsConsSites Score=880;Name=V$CEBPA_01 16 50756540 50756540 G C comments: rs2066845 (G908R), a non-synonymous SNP in NOD2
tfbsConsSites Score=878;Name=V$FREAC3_01 13 20763686 20763686 G - comments: rs1801002 (del35G), a frameshift mutation in GJB2, associated with hearing loss
tfbsConsSites Score=1000;Name=V$STAT4_01,V$AML1_01,V$SRY_01,V$MZF1_01 13 20797176 21105944 0 - comments: a 342kb deletion encompassing GJB6, associated with hearing loss
The second column again has the Score and Name annotation, which represents the normalized score and binding site motif name. Note that some caution should be taken when interpreting the results and users may want to filter the prediction data (for example, only consider variants within 1kb of transcription start site of genes as truly disrupting potential TFBS).
Note that the name such as V$PAX5_02 merely indicates a name for a motif that some transcription factors recognize. It is up to the user to investigate what transcription factors may recognize this motif. There are many online resources to help with this aspect, for example, MSigDB provides gene list that recognize these motifs, see for example http://www.broadinstitute.org/gsea/msigdb/cards/V$PAX5_02.
Identify cytogenetic band
To identify Giemsa-stained chromosomes bands, the -dbtype cytoBand can be used. The second column in the output file below represent cytogenetic bands. When a variant spans multiple bands, they will be connected by a dash (for example, 1q21.1-q23.3).
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ annotate_variation.pl -build hg19 -downdb cytoBand humandb/
NOTICE: Web-based checking to see whether ANNOVAR new version is available ... Done
NOTICE: Downloading annotation database http://hgdownload.cse.ucsc.edu/goldenPath/hg19/database/cytoBand.txt.gz ... OK
NOTICE: Uncompressing downloaded files
NOTICE: Finished downloading annotation files for hg19 build version, with files saved at the 'humandb' directory
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ annotate_variation.pl -regionanno -build hg19 -out ex1 -dbtype cytoBand example/ex1.avinput humandb/
NOTICE: Reading annotation database humandb/hg19_cytoBand.txt ... Done with 862 regions
NOTICE: Finished region-based annotation on 12 genetic variants in ex1.hg19.avinput
NOTICE: Output files were written to ex1.hg19_cytoBand
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ cat ex1.hg19_cytoBand
cytoBand 1q23.3 1 162736463 162736463 C T comments: rs1000050, a SNP in Illumina SNP arrays
cytoBand 1p31.1 1 84875173 84875173 C T comments: rs6576700 or SNP_A-1780419, a SNP in Affymetrix SNP arrays
cytoBand 1p36.21 1 13211293 13211294 TC - comments: rs59770105, a 2-bp deletion
cytoBand 1p36.22 1 11403596 11403596 - AT comments: rs35561142, a 2-bp insertion
cytoBand 1p21.1 1 105492231 105492231 A ATAAA comments: rs10552169, a block substitution
cytoBand 1p31.3 1 67705958 67705958 G A comments: rs11209026 (R381Q), a SNP in IL23R associated with Crohn's disease
cytoBand 2q37.1 2 234183368 234183368 A G comments: rs2241880 (T300A), a SNP in the ATG16L1 associated with Crohn's disease
cytoBand 16q12.1 16 50745926 50745926 C T comments: rs2066844 (R702W), a non-synonymous SNP in NOD2
cytoBand 16q12.1 16 50756540 50756540 G C comments: rs2066845 (G908R), a non-synonymous SNP in NOD2
cytoBand 16q12.1 16 50763778 50763778 - C comments: rs2066847 (c.3016_3017insC), a frameshift SNP in NOD2
cytoBand 13q12.11 13 20763686 20763686 G - comments: rs1801002 (del35G), a frameshift mutation in GJB2, associated with hearing loss
cytoBand 13q12.11 13 20797176 21105944 0 - comments: a 342kb deletion encompassing GJB6, associated with hearing loss
Identify variants disrupting microRNAs and snoRNAs
UCSC offers the wgRna table for snoRNA and microRNAs, based on the miRBase Release and snoRNABase. In ANNOVAR, since these are not real "gene definitions", they are therefore treated as region annotation databases, and we should use region annotation on them.
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ annotate_variation.pl -build hg19 -downdb wgRna humandb/
NOTICE: Web-based checking to see whether ANNOVAR new version is available ... Done
NOTICE: Downloading annotation database http://hgdownload.cse.ucsc.edu/goldenPath/hg19/database/wgRna.txt.gz ... OK
NOTICE: Uncompressing downloaded files
NOTICE: Finished downloading annotation files for hg19 build version, with files saved at the 'humandb' directory
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ annotate_variation.pl -regionanno -build hg19 -out ex1 -dbtype wgRna example/ex1.avinput humandb/
NOTICE: Reading annotation database humandb/hg19_wgRna.txt ... Done with 1341 regions
NOTICE: Finished region-based annotation on 12 genetic variants in ex1.hg19.avinput
NOTICE: Output files were written to ex1.hg19_wgRna
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ cat ex1.hg19_wgRna
In this case, none of the variants overlap with a microRNA or snoRNA.
Identify variants disrupting predicted microRNA binding sites
In addition to finding overlap to microRNAs, we can also find variants disrupting predicted microRNA binding sites. UCSC provides the TargetScanS annotation database, which shows conserved mammalian microRNA regulatory target sites for conserved microRNA families in the 3' UTR regions of Refseq Genes, as predicted by TargetScanHuman.
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ annotate_variation.pl -build hg19 -downdb targetScanS humandb/
NOTICE: Web-based checking to see whether ANNOVAR new version is available ... Done
NOTICE: Downloading annotation database http://hgdownload.cse.ucsc.edu/goldenPath/hg19/database/targetScanS.txt.gz ... OK
NOTICE: Uncompressing downloaded files
NOTICE: Finished downloading annotation files for hg19 build version, with files saved at the 'humandb' directory
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ annotate_variation.pl -regionanno -build hg19 -out ex1 -dbtype targetScanS example/ex1.avinput humandb/
NOTICE: Reading annotation database humandb/hg19_targetScanS.txt ... Done with 54199 regions
NOTICE: Finished region-based annotation on 12 genetic variants in ex1.hg19.avinput
NOTICE: Output files were written to ex1.hg19_targetScanS
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ cat ex1.hg19_targetScanS
In this case, none of the variants overlap with a microRNA target site.
Identify variants located in segmental duplications
Genetic variants that are mapped to segmental duplications are most likely sequence alignment errors and should be treated with extreme caution. Sometimes they manifest as SNPs with high fold coverage and probably high confidence score, but they may actually represent two non-polymorphic sites in the genomes that happen to have the same flanking sequence. To identify variants in these regions, use the command below. Again the first command download annotation databases, yet the second command identify variants in segmental duplications.
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/project/annotate_variation]$ annotate_variation.pl -build hg19 -downdb genomicSuperDups humandb/
NOTICE: Web-based checking to see whether ANNOVAR new version is available ... Done
NOTICE: Downloading annotation database http://hgdownload.cse.ucsc.edu/goldenPath/hg19/database/genomicSuperDups.txt.gz ... OK
NOTICE: Uncompressing downloaded files
NOTICE: Finished downloading annotation files for hg19 build version, with files saved at the 'humandb' directory
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/project/annotate_variation]$ annotate_variation.pl -regionanno -build hg19 -out ex1 -dbtype genomicSuperDups example/ex1.avinput humandb/
NOTICE: Reading annotation database humandb/hg19_genomicSuperDups.txt ... Done with 51599 regions
NOTICE: Finished region-based annotation on 12 genetic variants in ex1.hg19.avinput
NOTICE: Output files were written to ex1.hg19_genomicSuperDups
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/project/annotate_variation]$ cat ex1.hg19_genomicSuperDups
genomicSuperDups Score=0.99612;Name=chr1:13142561 1 13211293 13211294 TC - comments: rs59770105, a 2-bp deletion
The "Name" field in output represents the other "matching" segment in genome (which is located in the same chromosome at chr1:13142561). The "Score" field is the sequence identity with indels between two genomic segments (fracMatchIndel in the UCSC database table).
Identify previously reported structural variants
By using the --regionanno operation and the --dbtype dgvMerged, ANNOVAR can also conveniently annotate deletions and duplications and compare them to previously published variants in Database of Genomic Variants (DGV). Note that previously, the keyword dgv can be used in ANNOVAR, but UCSC no longer makes it available. For example,
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ annotate_variation.pl -build hg19 -downdb dgvMerged humandb/
NOTICE: Web-based checking to see whether ANNOVAR new version is available ... Done
NOTICE: Downloading annotation database http://hgdownload.cse.ucsc.edu/goldenPath/hg19/database/dgvMerged.txt.gz ... OK
NOTICE: Uncompressing downloaded files
NOTICE: Finished downloading annotation files for hg19 build version, with files saved at the 'humandb' directory
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ annotate_variation.pl -regionanno -build hg19 -out ex1 -dbtype dgvMerged example/ex1.avinput humandb/
NOTICE: Reading annotation database humandb/hg19_dgvMerged.txt ... Done with 202430 regions
NOTICE: Finished region-based annotation on 12 genetic variants in ex1.hg19.avinput
NOTICE: Output files were written to ex1.hg19_dgvMerged
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ cat ex1.hg19_dgvMerged
dgvMerged Name=nsv516482 1 162736463 162736463 C T comments: rs1000050, a SNP in Illumina SNP arrays
dgvMerged Name=nsv830437 1 84875173 84875173 C T comments: rs6576700 or SNP_A-1780419, a SNP in Affymetrix SNP arrays
dgvMerged Name=dgv168n71,nsv821616,nsv510936,nsv871634,esv27872,nsv870885,dgv147n71,nsv517190,nsv821333,nsv871687,nsv7172,nsv428410,nsv8768,dgv20e1,dgv22e1 1 13211293 13211294 TC - comments: rs59770105, a 2-bp deletion
dgvMerged Name=nsv832536 1 11403596 11403596 - AT comments: rs35561142, a 2-bp insertion
dgvMerged Name=nsv830937 1 105492231 105492231 A ATAAA comments: rs10552169, a block substitution
dgvMerged Name=nsv1243 1 67705958 67705958 G A comments: rs11209026 (R381Q), a SNP in IL23R associated with Crohn's disease
dgvMerged Name=nsv899871 13 20763686 20763686 G - comments: rs1801002 (del35G), a frameshift mutation in GJB2, associated with hearing loss
dgvMerged Name=esv259791,esv1000311,esv25857,esv2751132,nsv821552,nsv517163,dgv314n67,dgv221n27,nsv524401,esv27122,esv2747059,esv2747061,nsv826576,esv2675972,nsv899871, dgv240e201,esv2747062,nsv899873,nsv826577,dgv1555n71,esv2747060,nsv818947,esv1659805,dgv545e1,esv7898,esv1680496,esv2747066,esv34984,dgv1554n71,nsv527067 13 20797176 21105944 0 - comments: a 342kb deletion encompassing GJB6, associated with hearing loss
The above command identifies 3 variants located in previously reported structural variation regions in Database of Genomic Variants. Their scores are all zero, because score is not defined for DGV track. The Name represent DGV database identifiers for CNVs. The GJB6 deletion overlaps with a few different entries in the DGV.
For structural variants such as deletions and duplications, the -minqueryoverlap may be very useful (otherwise many SNPs/indels will overlap with a DGV region). It requires that at least this percentage of query be overlapped with a database entry.
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ annotate_variation.pl -regionanno -build hg19 -out ex1 -dbtype dgvMerged example/ex1.avinput humandb/ -minqueryfrac 0.5
NOTICE: Reading annotation database humandb/hg19_dgvMerged.txt ... Done with 202430 regions
NOTICE: Finished region-based annotation on 12 genetic variants in ex1.hg19.avinput
NOTICE: Output files were written to ex1.hg19_dgvMerged
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ cat ex1.hg19_dgvMerged
dgvMerged Name=nsv516482 1 162736463 162736463 C T comments: rs1000050, a SNP in Illumina SNP arrays
dgvMerged Name=nsv830437 1 84875173 84875173 C T comments: rs6576700 or SNP_A-1780419, a SNP in Affymetrix SNP arrays
dgvMerged Name=dgv168n71,nsv821616,nsv510936,nsv871634,esv27872,nsv870885,dgv147n71,nsv517190,nsv821333,nsv871687,nsv7172,nsv428410,nsv8768,dgv20e1,dgv22e1 1 13211293 13211294 TC - comments: rs59770105, a 2-bp deletion
dgvMerged Name=nsv832536 1 11403596 11403596 - AT comments: rs35561142, a 2-bp insertion
dgvMerged Name=nsv830937 1 105492231 105492231 A ATAAA comments: rs10552169, a block substitution
dgvMerged Name=nsv1243 1 67705958 67705958 G A comments: rs11209026 (R381Q), a SNP in IL23R associated with Crohn's disease
dgvMerged Name=nsv899871 13 20763686 20763686 G - comments: rs1801002 (del35G), a frameshift mutation in GJB2, associated with hearing loss
dgvMerged Name=esv2751132 13 20797176 21105944 0 - comments: a 342kb deletion encompassing GJB6, associated with hearing loss
As we can see from the results above, adding a -minqueryfrac 0.5 argument reduces the number of database hits (now only esv2751132 is shown in the Name field for the 342kb deletion). To understand this more, check the genome browser shots for this region:
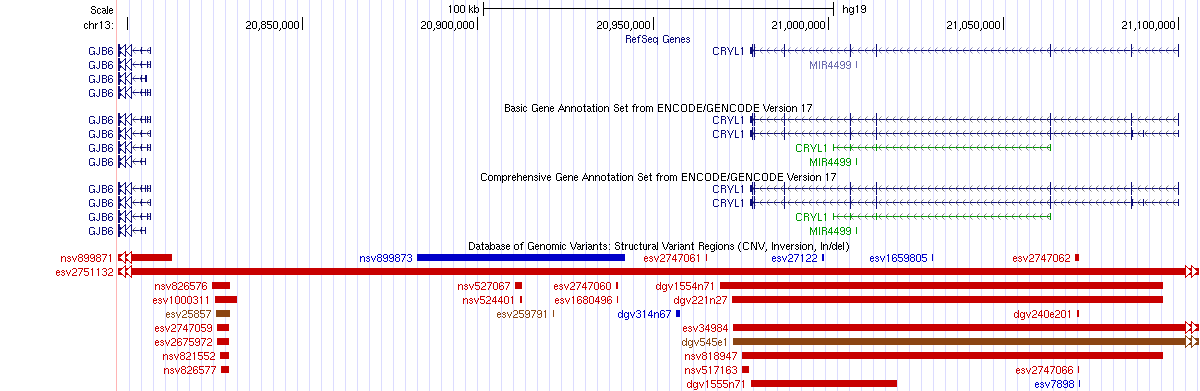
The above figure shows that this query region overlaps with several CNVs reported in DGV, but only one of them (identifier is esv2751132) contains more than 50% of the query.
Identify variants reported in previously published GWAS
To find variants that were previously reported to be associated with diseases or traits in genome-wide association studies, the gwasCatalog keyword can be used:
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ annotate_variation.pl -build hg19 -downdb gwasCatalog humandb/
NOTICE: Web-based checking to see whether ANNOVAR new version is available ... Done
NOTICE: Downloading annotation database http://hgdownload.cse.ucsc.edu/goldenPath/hg19/database/gwasCatalog.txt.gz ... OK
NOTICE: Uncompressing downloaded files
NOTICE: Finished downloading annotation files for hg19 build version, with files saved at the 'humandb' directory
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ annotate_variation.pl -regionanno -build hg19 -out ex1 -dbtype gwasCatalog example/ex1.avinput humandb/
NOTICE: Reading annotation database humandb/hg19_gwasCatalog.txt ... Done with 18435 regions
NOTICE: Finished region-based annotation on 12 genetic variants in ex1.hg19.avinput
NOTICE: Output files were written to ex1.hg19_gwasCatalog
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ cat ex1.hg19_gwasCatalog
gwasCatalog Name=Ankylosing spondylitis,Crohn's disease,Ulcerative colitis,Psoriasis,Inflammatory bowel disease 1 67705958 67705958 comments: rs11209026 (R381Q), a SNP in IL23R associated with Crohn's disease
gwasCatalog Name=Crohn's disease 2 234183368 234183368 A G comments: rs2241880 (T300A), a SNP in the ATG16L1 associated with Crohn's disease
gwasCatalog Name=Crohn's disease 16 50763778 50763778 - C comments: rs2066847 (c.3016_3017insC), a frameshift SNP in NOD2
The above command identifies 3 variants previously reported in GWAS (note that the IL23R variant is known to be associated with multiple diseases already, but the gwasCatalog track is not that comprehensive yet).
Identify variants in ENCODE annotated regions
ENCODE now provides huge amounts of data in Genome Browser tracks that ANNOVAR can annotate against, such as transcribed regions, H3K4Me1 regions, H3K4Me3 regions, H3K27Ac regions, DNaseI hypersensitivity regions, transcription factor ChIP-Seq regions, etc. Some specific examples are shown below, but obviously, there are hundreds of ENCODE annotation tracks that can be used in ANNOVAR.
Technical Notes: Although UCSC may provide more ENCODE annotations for hg19 in the future, at least at end of 2013 rich annotation is only available for hg18. The examples below all used hg18. If you are interested to annotate your hg19 variants, some of these databases may not be available and you should check Table Browser yourself to know what is available and what is not. If you absolutely need to use these specific tables, it is best that you liftOver the database yourself to hg19 for annotation.
A general rule of thumb is that:
- active promoter: H3K4me3, H3K9Ac
- active enhancer: H3K4me1, H3K27Ac
- active elongation: H3K36me3, H3K79me2
- repressed promoters and broad regions: H3K27me3, H3K9me3
To check whether the variants are located in transcribed regions in the RNA-Seq data for GM12878 cell lines:
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ annotate_variation.pl -downdb wgEncodeCaltechRnaSeqRawSignalRep1Gm12878CellLongpolyaBb12x75 humandb/
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ annotate_variation.pl -regionanno -dbtype wgEncodeCaltechRnaSeqRawSignalRep1Gm12878CellLongpolyaBb12x75 -out ex1 ex1.hg18.avinput humandb/
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ wc -l ex1.hg18_wgEncodeCaltechRnaSeqRawSignalRep1Gm12878CellLongpolyaBb12x75
7 ex1.human.hg18_wgEncodeCaltechRnaSeqRawSignalRep1Gm12878CellLongpolyaBb12x75
So 7 of of the 12 regions in ex1.hg18.avinput are transcribed in the GM12878 cell lines. Note that here we used RawSignal; it may make sense to use summarized signals that impose a specific expression activity threshold to eliminate lowly-expressed genes.
To check whether the variants are located in enhancer regions, based on H3K4Me1 (or H3K27Ac if you want) chromatin marks in GM12878 cells:
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ annotate_variation.pl -downdb wgEncodeBroadChipSeqPeaksGm12878H3k4me1 humandb/
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ annotate_variation.pl -regionanno -dbtype wgEncodeBroadChipSeqPeaksGm12878H3k4me1 -out ex1 ex1.hg18.avinput humandb/ -scorecolumn 5
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ cat ex1.hg18_wgEncodeBroadChipSeqPeaksGm12878H3k4me1
wgEncodeBroadChipSeqPeaksGm12878H3k4me1 Score=1000;Name=. 16 49303427 49303427 C T comments: rs2066844 (R702W), a non-synonymous SNP in NOD2
wgEncodeBroadChipSeqPeaksGm12878H3k4me1 Score=1000;Name=. 13 19695176 20003944 0 - comments: a 342kb deletion encompassing GJB6, associated with hearing loss
2 out of the 12 variants are considered to be in enhancers. The Name is "." because ENCODE did not assign a name to these regions. Note that in the command above, we used -scorecolumn 5, to tell the program that the fifth column is the score column.
To check whehter the variants are located in DNase I hypersensitivity sites from ENCODE:
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ annotate_variation.pl -downdb wgEncodeRegDnaseClustered humandb/
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ annotate_variation.pl -regionanno -dbtype wgEncodeRegDnaseClustered ex1.hg18.avinput humandb/ -scorecolumn 5 -out ex1
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ cat ex1.hg18_wgEncodeRegDnaseClustered
wgEncodeRegDnaseClustered Score=446;Name=5 16 49303427 49303427 C T comments: rs2066844 (R702W), a non-synonymous SNP in NOD2
wgEncodeRegDnaseClustered Score=1000;Name=25,64,9,15,56,45,19,23,13 13 19695176 20003944 0 - comments: a 342kb deletion encompassing GJB6, associated with hearing loss
As an exercise, the users should try to annotate CTCF binding site (hint: use -dbtype wgEncodeBroadChipSeqPeaksGm12878Ctcf).
To annotate ENCODE transcription factor ChIP-Seq data:
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ annotate_variation.pl -downdb wgEncodeRegTfbsClustered humandb/
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ annotate_variation.pl -regionanno -dbtype wgEncodeRegTfbsClustered ex1.hg18.avinput humandb/ -scorecolumn 5 -out ex1
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ cat ex1.hg18_wgEncodeRegTfbsClustered
wgEncodeRegTfbsClustered Score=305;Name=NRSF 16 49303427 49303427 C T comments: rs2066844 (R702W), a non-synonymous SNP in NOD2
wgEncodeRegTfbsClustered Score=1000;Name=BAF155,EBF,IRF4,BATF,TCF12,Max,BAF170,PU.1,JunD,c-Jun,GR,Egr-1,BCL3,PAX5-N19,BCL11A,NFKB,Ini1,PAX5-C20 13 19695176 20003944 0 - comments: a 342kb deletion encompassing GJB6, associated with hearing loss
Note that the 342kb deletion encompass multiple binding sites, just because of its large size.
Identify dbSNP variants in user-specified regions
This is straightfoward, by using -dbtype snp138 together with -regionanno opeartion. Note that -regionanno only cares about region overlap, whereas -filter cares about exact region and exact base pair identities.
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ annotate_variation.pl ex1.hg18.avinput humandb/ -region -dbtype snp138 -out ex1
Now check the ex1.hg18_snp138 output file. For each input line, it listed whether this line contains one or more known dbSNP entries. The 300kb deletion has many SNPs inside.
This is different from filter-based annotation. Here, we only cares about if two regions have overlap, rather than being identical. Therefore, the deletion region can match to multiple SNPs in the dbSNP database.
Identify non-coding variants that disrupt enhancers, repressors, promoters
There are multiple ways in which users can accomplish this goal. For example, users can follow the ENCODE annotation instructions above.
Users can also use chromHMM predictions to annotate and classify non-coding variants into enhancers, repressors, promoters, insulators, etc. First, select a cell line of interest, from the following choices.
| Cell | Description | Lineage | Tissue | Karyotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GM12878 | B-lymphocyte, lymphoblastoid, International HapMap Project - CEPH/Utah - European Caucasion, Epstein-Barr Virus | mesoderm | blood | normal |
| H1-hESC | embryonic stem cells | inner cell mass | embryonic stem cell | normal |
| K562 | leukemia, "The continuous cell line K-562 was established by Lozzio and Lozzio from the pleural effusion of a 53-year-old female with chronic myelogenous leukemia in terminal blast crises." - ATCC | mesoderm | blood | cancer |
| HepG2 | hepatocellular carcinoma | endoderm | liver | cancer |
| HUVEC | umbilical vein endothelial cells | mesoderm | blood vessel | normal |
| HMEC | mammary epithelial cells | ectoderm | breast | normal |
| HSMM | skeletal muscle myoblasts | mesoderm | muscle | normal |
| NHEK | epidermal keratinocytes | ectoderm skin | normal | |
| NHLF | lung fibroblasts | endoderm | lung | normal |
Then download the HMM predictions for this cell line. Then annotate against the HMM predictions by region-based annotation.
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ annotate_variation.pl ex1.hg18.avinput humandb/ -regionanno -dbtype wgEncodeBroadHmmGm12878HMM -out ex1
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ cat ex1.hg18_wgEncodeBroadHmmGm12878HMM
wgEncodeBroadHmmGm12878HMM Name=13 Heterochrom/lo 1 161003087 161003087 C T comments: rs1000050, a SNP in Illumina SNP arrays
wgEncodeBroadHmmGm12878HMM Name=13 Heterochrom/lo 1 84647761 84647761 C T comments: rs6576700 or SNP_A-1780419, a SNP in Affymetrix SNP arrays
wgEncodeBroadHmmGm12878HMM Name=13 Heterochrom/lo 1 13133880 13133881 TC - comments: rs59770105, a 2-bp deletion
wgEncodeBroadHmmGm12878HMM Name=13 Heterochrom/lo 1 11326183 11326183 - AT comments: rs35561142, a 2-bp insertion
wgEncodeBroadHmmGm12878HMM Name=13 Heterochrom/lo 1 105293754 105293754 A ATAAA comments: rs10552169, a block substitution
wgEncodeBroadHmmGm12878HMM Name=11 Weak Txn 1 67478546 67478546 G A comments: rs11209026 (R381Q), a SNP in IL23R associated with Crohn's disease
wgEncodeBroadHmmGm12878HMM Name=10 Txn Elongation 2 233848107 233848107 A G comments: rs2241880 (T300A), a SNP in the ATG16L1 associated with Crohn's disease
wgEncodeBroadHmmGm12878HMM Name=10 Txn Elongation 16 49303427 49303427 C T comments: rs2066844 (R702W), a non-synonymous SNP in NOD2
wgEncodeBroadHmmGm12878HMM Name=10 Txn Elongation 16 49314041 49314041 G C comments: rs2066845 (G908R), a non-synonymous SNP in NOD2
wgEncodeBroadHmmGm12878HMM Name=10 Txn Elongation 16 49321279 49321279 - C comments: rs2066847 (c.3016_3017insC), a frameshift SNP in NOD2
wgEncodeBroadHmmGm12878HMM Name=12 Repressed 13 19661686 19661686 G - comments: rs1801002 (del35G), a frameshift mutation in GJB2, associated with hearing loss
wgEncodeBroadHmmGm12878HMM Name=12 Repressed,4 Strong Enhancer,2 Weak Promoter,3 Poised Promoter,1 Active Promoter,6 Weak Enhancer,8 Insulator,13 Heterochrom/lo,15 Repetitive/CNV,14 Repetitive/CNV,7 Weak Enhancer,11 Weak Txn,5 Strong Enhancer 13 19695176 20003944 0 - comments: a 342kb deletion encompassing GJB6, associated with hearing loss
The details of the HMM state definition can be found below. The prediction is given in the "Name" field (second column in the output file). In the result above, the GJB6 deletion emcompasses multiple elements, including repressor, enhancer, promoter and so on. The rs11209026 SNP covers a weak transcriptional unit. The SNPs in NOD2 overlaps transcriptional elongation elements, the frameshift mutation in GJB2 covers a repressor, and other SNPs cover heterochromatin regions.
- State 1 - Active Promoter
- State 2 - Weak Promoter
- State 3 - Inactive/poised Promoter
- State 4 - Strong enhancer
- State 5 - Strong enhancer
- State 6 - Weak/poised enhancer
- State 7 - Weak/poised enhancer
- State 8 - Insulator
- State 9 - Transcriptional transition
- State 10 - Transcriptional elongation
- State 11 - Weak transcribed
- State 12 - Polycomb-repressed
- State 13 - Heterochromatin; low signal
- State 14 - Repetitive/Copy Number Variation
- State 15 - Repetitive/Copy Number Variation
For example, the rs1801002 mutation was predicted to be in state 12 (polycomb-repressed region) above in GM12878 cells, even though it is also a coding mutation. We can confirm this observation in the Genome Browser shot below. It is interesting to see that it serves different functions in different cell lines (but of course everything is based on prediction and this may or may not be reliable).
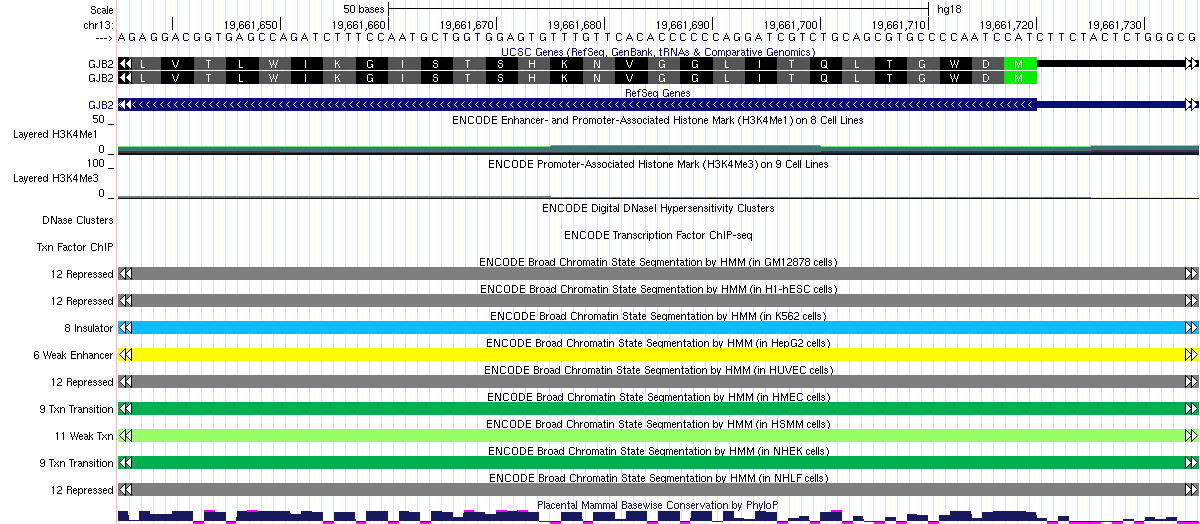
Identify variants in other genomic regions annotated with other functions
If you use UCSC database for the annotation, in principle, the vast majority of tracks (hundreds) conforming to the standard file format can be handled by ANNOVAR.
For example, say I want to identify whether a variant is located in a "hot spot" of DNAse I hypersensitivity sites in the GM12878 cell line (which is a model cell line). These sites mark activated cis-regulatory regions including promoters, enhancers, insulators. The following command will do it:
[kai@biocluster ~/]$ annotate_variation.pl -downdb wgEncodeUwDnaseSeqHotspotsRep2Gm12878 humandb/
[kai@biocluster ~/]$ annotate_variation.pl -region ex1.hg18.avinput humandb/ -dbtype wgEncodeUwDnaseSeqHotspotsRep2Gm12878 -out ex1
[kai@biocluster ~/]$ cat ex1.hg18_wgEncodeUwDnaseSeqHotspotsRep2Gm12878
wgEncodeUwDnaseSeqHotspotsRep2Gm12878 Score=549 13 19695176 20003944 0 - comments: a 342kb deletion encompassing GJB6, associated with hearing loss
Users can change "hotspot" to "peaks" to find the most significant hypersensitivity sites among the zones, and change GM12878 to dozens of other cell lines to identify these regions in other lines. The possibility is limited only by the current database annotation, as well as the genomic regions that have been assayed.
Annotating custom-made databases conforming to GFF3 (Generic Feature Format version 3)
ANNOVAR also offer some rudimentary ability to annotate variants against GFF3-formatted annotation databases, using the region-based annotation procedure. In this case, the -dbtype is 'gff3', but users need to specify a -gff3dbfile argument as well to supply the actual database file to be scanned. The GFF3 format specification is described here: http://www.sequenceontology.org/gff3.shtml. One example database is provided in the ANNOVAR package:
[kai@biocluster ~/]$ head humandb/hg18_example_db_gff3.txt
##gff-version 3
chr1 tfloc TF_binding_site 83024 83039 849 - . ID=pos83031;Name=V$FREAC3_01
chr1 tfloc TF_binding_site 229352 229367 849 - . ID=pos229359;Name=V$FREAC3_01
chr1 tfloc TF_binding_site 405674 405689 849 + . ID=pos405681;Name=V$FREAC3_01
chr1 tfloc TF_binding_site 564503 564518 849 - . ID=pos564510;Name=V$FREAC3_01
chr1 tfloc TF_binding_site 1103849 1103864 847 - . ID=pos1103856;Name=V$FREAC3_01
chr1 tfloc TF_binding_site 1311968 1311983 917 - . ID=pos1311975;Name=V$FREAC3_01
chr1 tfloc TF_binding_site 2160490 2160505 818 - . ID=pos2160497;Name=V$FREAC3_01
chr1 tfloc TF_binding_site 2229446 2229461 924 - . ID=pos2229453;Name=V$FREAC3_01
chr1 tfloc TF_binding_site 2229639 2229654 842 - . ID=pos2229646;Name=V$FREAC3_01
To examine which query fall into the regions specified in GFF3 database:
[kai@biocluster ~/]$ annotate_variation.pl -regionanno -dbtype gff3 -gff3dbfile hg18_example_db_gff3.txt ex1.hg18.avinput humandb/ -out ex1
NOTICE: The --buildver is set as 'hg18' by default
NOTICE: Reading annotation database humandb/hg18_example_db_gff3.txt ... Done with 25691 regions
NOTICE: Finished region-based annotation on 12 genetic variants in ex1.human
NOTICE: Output files were written to ex1.hg18_gff3
[kai@biocluster ~/]$ cat ex1.hg18_gff3
gff3 Score=878;Name=19661681 13 19661686 19661686 G - comments: rs1801002 (del35G), a frameshift mutation in GJB2, associated with hearing loss
gff3 Score=859;Name=19695580 13 19695176 20003944 0 - comments: a 342kb deletion encompassing GJB6, associated with hearing loss
Based on the above results, two variants disrupt annotated regions in the GFF3 database file. Note that the "Name" in output corresponds to "ID" in the original GFF3 file (based on GFF3 specification, ID for every record must be unique within a file, so this is the only identifier that can uniquely identify a specific region).
Starting from Feb 2013, I begin to include several "sample" GFF3 files in the ANNOVAR distribution package, which were provided by BioBase and represent a small fraction of the GenomeTrax annotation databases. ANNOVAR can be used to annotate these files. For example:
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ annotate_variation.pl -region -dbtype gff3 -gff3dbfile sample_transfac_sites_featuretype_hg19.gff -buildver hg19 inputfile genometrax-sample-files-gff/
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ cat inputfile.hg19_gff3
gff3 Name=158596383 22 27017833 27017833 A C
will find variants that fall within TRANSFAC regions. The output will include the identifier of the TRANSFAC region, but if you want to see more details in the output, add the --gff3attr argument.
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ annotate_variation.pl -region -dbtype gff3 -gff3dbfile sample_transfac_sites_featuretype_hg19.gff -buildver hg19 -gff3attr inputfile genometrax-sample-files-gff/
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ cat inputfile.hg19_gff3
gff3 ID=158596383; accession=R28160; bindingFactor=c-MAF_MOUSE; ensembl=N/A; entrez=N/A; hgnc=N/A; hyperlink=https://portal.biobase-international.com/cgi-bin/build_gtrx/idb/1.0/pageview.cgi?view%3DSiteReport&site_acc%3DR28160; pmid=9616139; siteAcc=R28160; uniprot=N/A; feature=R28160:c-MAF_MOUSE 22 270178327017833 A C
You will see that the output file now contains all relevant information for this particular transcription factor binding site.
Identifying variants in regions specified in BED files
Sometimes you may get a BED file from somewhere and want to know if some of the variants fall within the regions specified in BED. For example, after an exome sequencing experiments, you identified many variants, but want to focus on variants that only fall within the designed exome capture regions. Typically, capture array manufacturers will provide the regions in BED file. ANNOVAR provides the means to use the BED file as database directly.
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ annotate_variation.pl ex1.hg18.avinput humandb/ -bedfile hg18_SureSelect_All_Exon_G3362_with_names.bed -dbtype bed -regionanno -out ex1
NOTICE: The --buildver is set as 'hg18' by default
NOTICE: Reading annotation database hg18_SureSelect_All_Exon_G3362_with_names.bed ... Done with 165637 regions
NOTICE: Finished region-based annotation on 12 genetic variants in ex1.human
NOTICE: Output files were written to ex1.hg18_bed
[kaiwang@biocluster ~/]$ cat ex1.hg18_bed
bed Name=NA 1 67478546 67478546 G A comments: rs11209026 (R381Q), a SNP in IL23R associated with Crohn's disease
bed Name=NA 2 233848107 233848107 A G comments: rs2241880 (T300A), a SNP in the ATG16L1 associated with Crohn's disease
bed Name=NA 16 49303427 49303427 C T comments: rs2066844 (R702W), a non-synonymous SNP in NOD2
bed Name=NA 16 49314041 49314041 G C comments: rs2066845 (G908R), a non-synonymous SNP in NOD2
bed Name=NA 16 49321279 49321279 - C comments: rs2066847 (c.3016_3017insC), a frameshift SNP in NOD2
bed Name=NA 13 19661686 19661686 G - comments: rs1801002 (del35G), a frameshift mutation in GJB2, associated with hearing loss
bed Name=NA 13 19695176 20003944 0 - comments: a 342kb deletion encompassing GJB6, associated with hearing loss
In the output, "Name=NA" because there is no such annotation in a typical BED file.
The -colsWanted argument can be used to specify which column or columns should be included in the output. For example, -colsWanted 4,5,6 means the column 4, 5 and 6 should be in the output (assuming that your BED file has at least 6 columns). You can also use -colsWanted all to specify that all columns be printed out. When multiple columns are printed out, they will be comma-delimited.